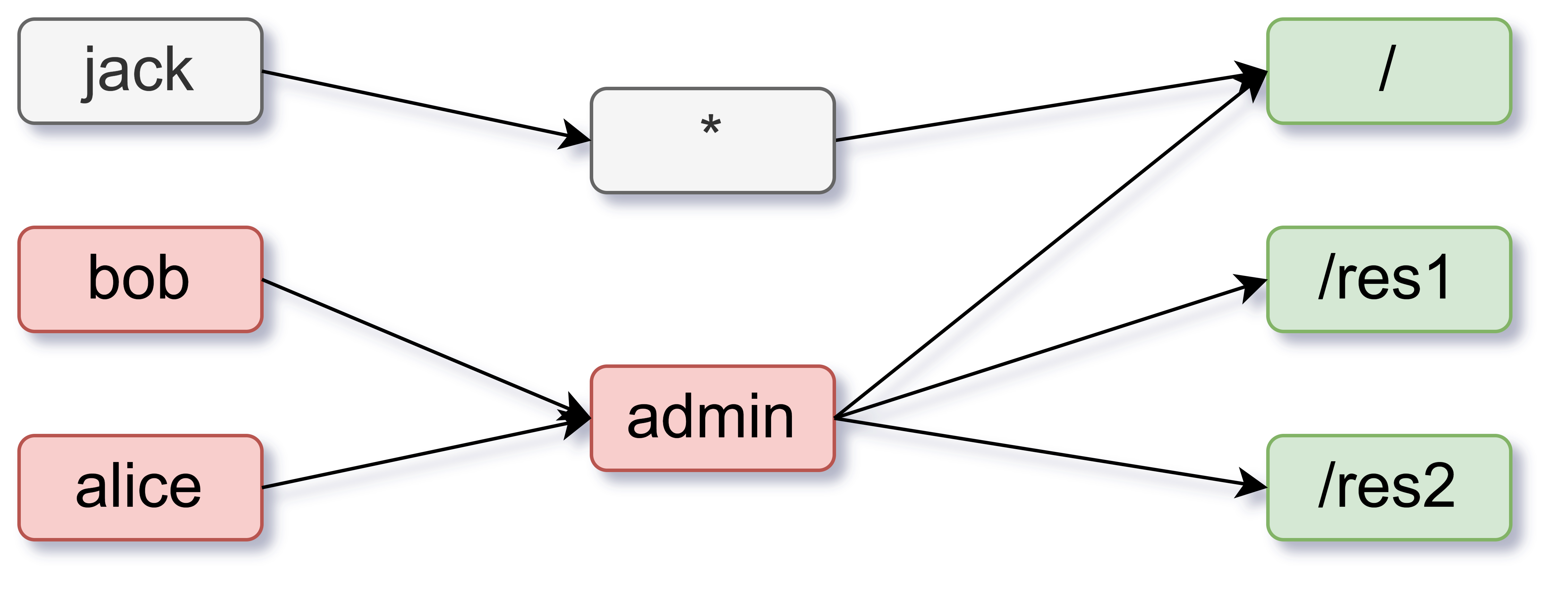
In this post, I will explain the design and implementation of RBAC using the Casbin library. For a SaaS platform dealing with multiple resource hierarchies and roles that inherit permissions from higher levels, Casbin provides a performant alternative to consider.
RBAC is a method of restricting access to resources based on the roles that individuals hold. To better understand how hierarchical RBAC works, let's take a look at Azure's RBAC system in the next section and then attempt to implement a similar system.
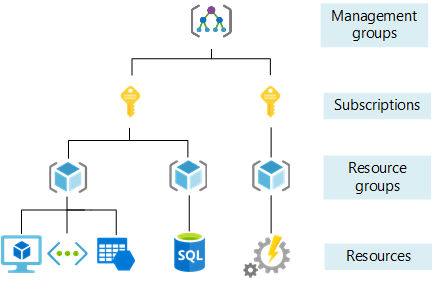
There is a role called Owner for all resources in Azure. Suppose if I have the Owner role assigned to me at the
subscription level, that means I am the Owner of all the resource groups and resources under that subscription. If I have
Owner at the resource group level, then I am the Owner of all the resources under that resource group.
This image shows that I have Owner access at the subscription level. 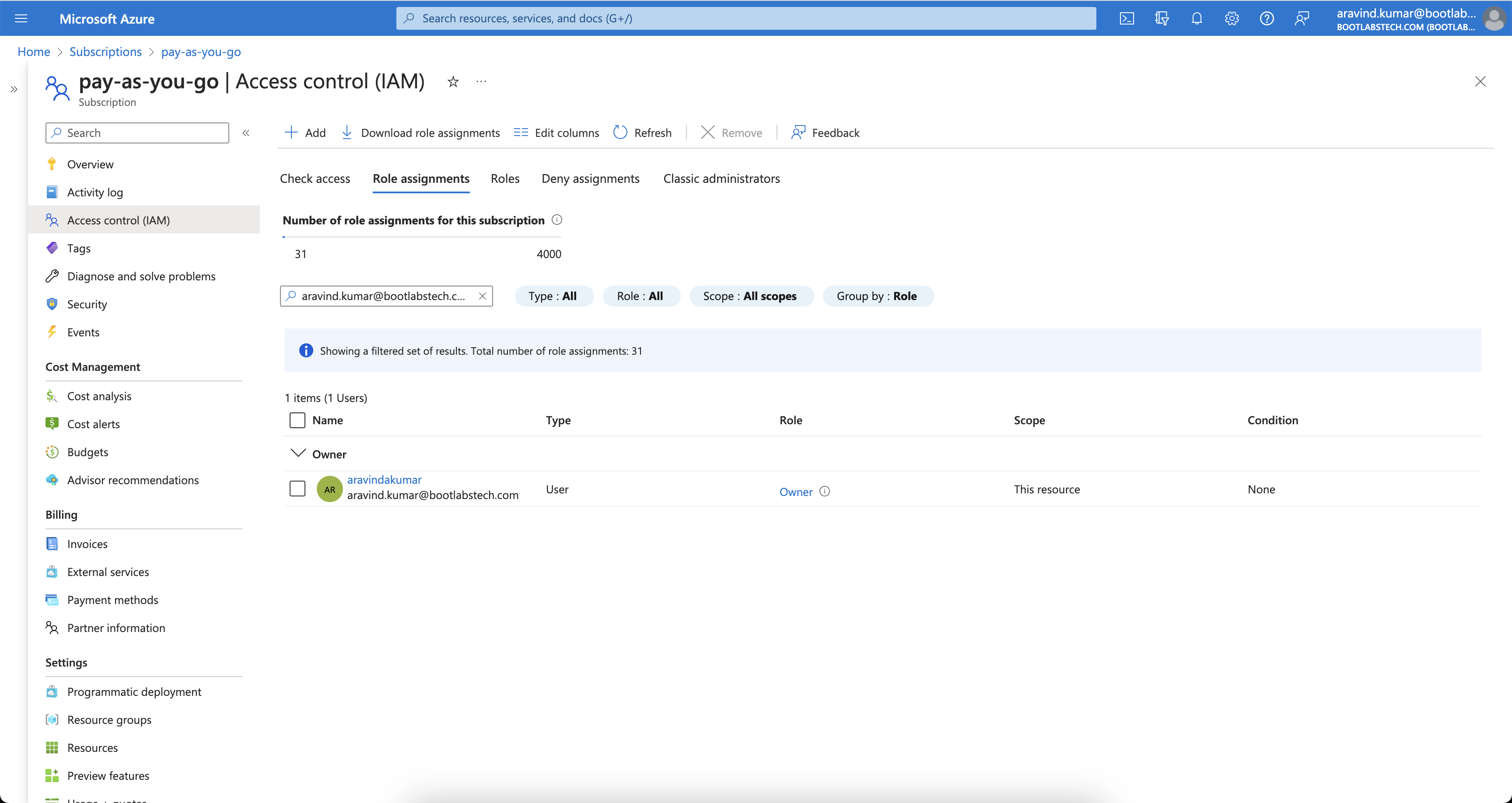
When I check the IAM of a Resource Group under this Subscription, you can see that I have inherited Owner access from the
subscription. 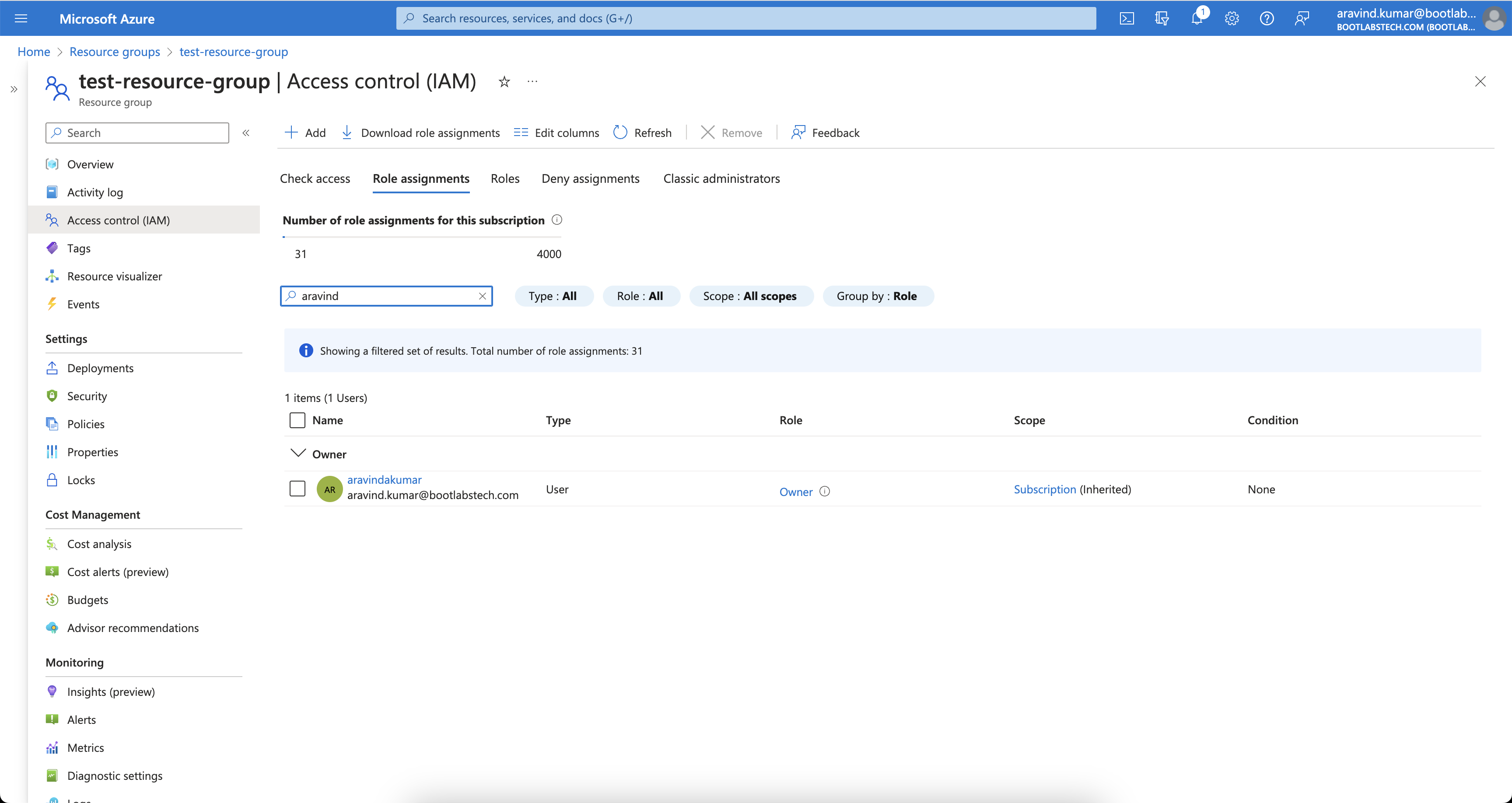
So, this is how Azure's RBAC is hierarchical. Most enterprise software uses hierarchical RBAC because of the hierarchical
nature of the resource levels. In this tutorial, we'll try to implement a similar system using Casbin.
Before diving into the implementation, it is important to understand what Casbin is and how it functions at a high level. This understanding is necessary because each Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) system may vary based on specific requirements. By grasping the workings of Casbin, we can effectively fine-tune the model.
ACL stands for Access Control List. It is a method in which users are mapped to actions and actions to resources.
Let's consider a simple example of an ACL model.
[request_definition]
r = sub, act, obj
[policy_definition]
p = sub, act, obj
[policy_effect]
e = some(where (p.eft == allow))
[matchers]
m = r.sub == p.sub && r.obj == p.obj && r.act == p.act
-
The request_definition is the query template of the system. For example, a request alice, write, data1 can be
interpreted as "Can subject Alice perform the action 'write' on object 'data1'?".
-
The policy_definition is the assignment template of the system. For example, by creating a policy alice, write, data1, you are
assigning permission to subject Alice to perform the action 'write' on object 'data1'.
-
The policy_effect defines the effect of the policy.
-
In the matchers section, the request is matched with the policy using the conditions r.sub == p.sub && r.obj == p.obj && r.act == p.act.
Open the editor and paste the above model in the Model editor.
Paste the following in the Policy editor:
p, alice, read, data1
p, bob, write, data2
and the following in the Request editor:
The result will be:
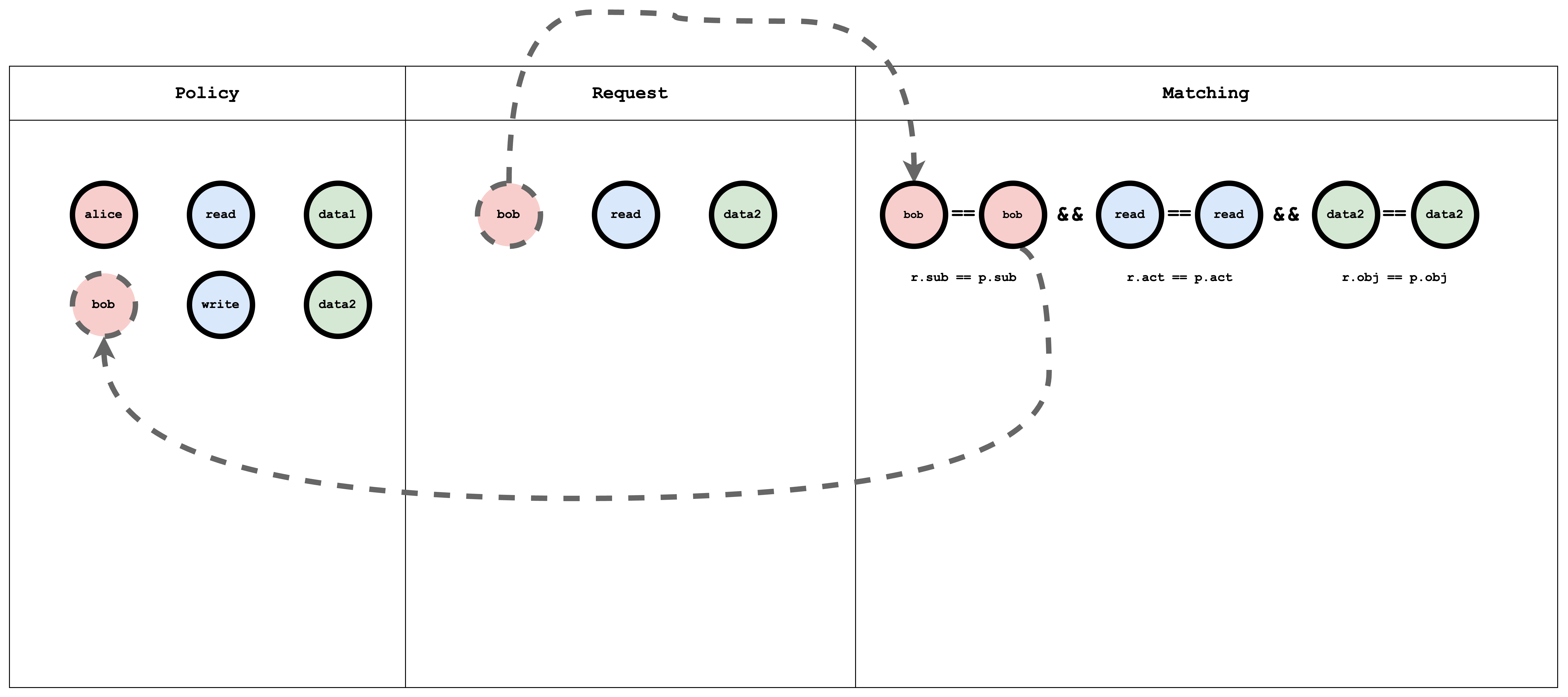
RBAC stands for Role-Based Access Control. In RBAC, a user is assigned a role for a resource, and a role can contain arbitrary actions. The request then checks if the user has the permission to perform the action on the resource.
Let's consider a simple example RBAC model:
[request_definition]
r = sub, act, obj
[policy_definition]
p = sub, act, obj
[role_definition]
g = _, _
g2 = _, _
[policy_effect]
e = some(where (p.eft == allow))
[matchers]
m = r.sub == p.sub && g(p.act, r.act) && r.obj == p.obj
- The role_definition is a graph relation builder that uses a Graph to compare the request object with the policy object.
Open the editor and paste the above model in the Model editor.
Paste the following in the Policy editor:
p, alice, reader, data1
p, bob, owner, data2
g, reader, read
g, owner, read
g, owner, write
and the following in the Request editor:
alice, read, data1
alice, write, data1
bob, write, data2
bob, read, data2
bob, write, data1
The result will be:
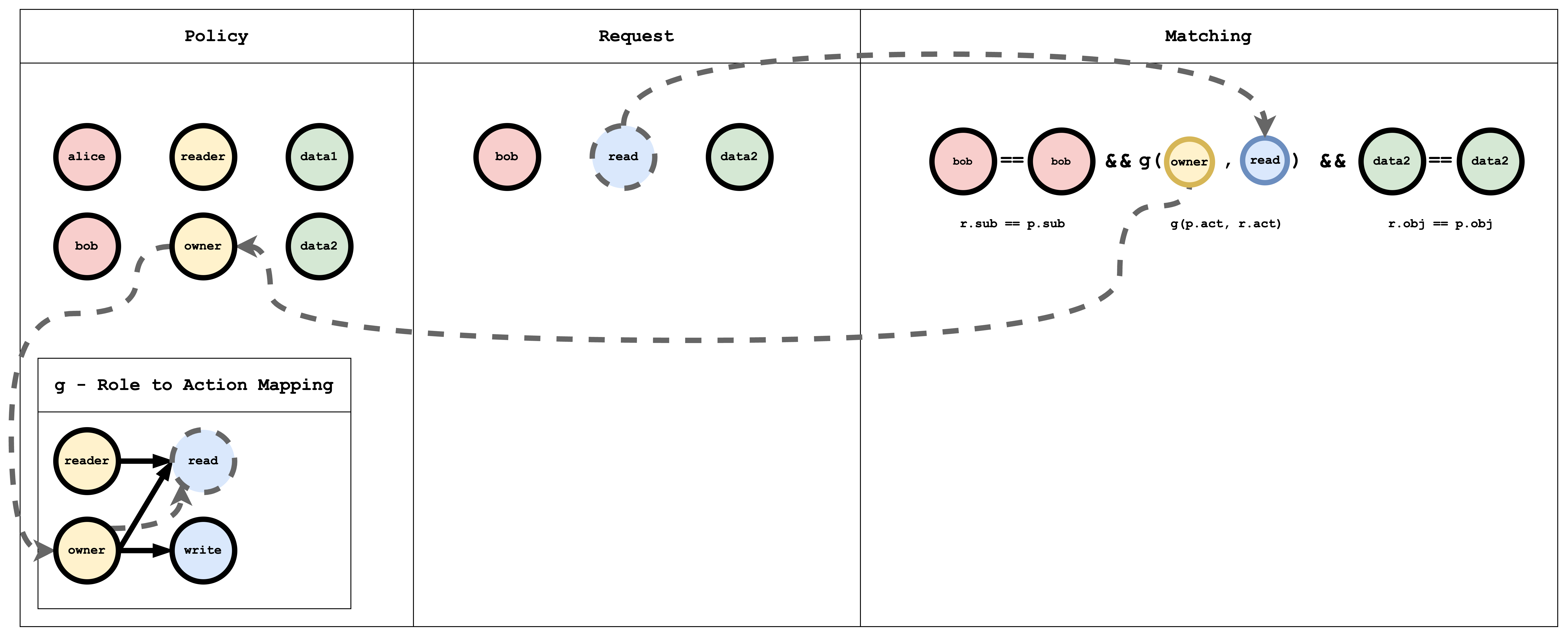
The g - Role to action mapping table has a Graph mapping the role to action. This Graph can be coded as a list of edges, as shown in the policy which is a common way of representing a Graph:
g, reader, read
g, owner, read
g, owner, write
p indicates a normal policy that can be compared using the == operator. g is a Graph-based comparison function. You can define multiple Graph comparators by adding a numerical suffix like g, g2, g3, ... and so on.
In Hierarchical RBAC, there are more than one type of resources and there is an inheritance relationship between the resource types. For example, "subscription" is one type and "resourceGroup" is another type. A sub1 of type Subscription can contain multiple resourceGroups (rg1, rg2) of type ResourceGroup.
Similar to the resource hierarchy, there will be two types of roles and actions: Subscription roles and actions, and ResourceGroup roles and actions. There is an arbitrary relationship between the Subscription role and ResourceGroup role. For example, consider a Subscription Role sub-owner. This role is inherited by a ResourceGroup Role rg-owner, which means that if I am assigned the sub-owner role on Subscription sub1, then I automatically also get the rg-owner role on rg1 and rg2.
Let's take a simple example of the Hierarchical RBAC model:
[request_definition]
r = sub, act, obj
[policy_definition]
p = sub, act, obj
[role_definition]
g = _, _
g2 = _, _
[policy_effect]
e = some(where (p.eft == allow))
[matchers]
m = r.sub == p.sub && g(p.act, r.act) && g2(p.obj, r.obj)
- The role_definition is a graph relation builder which uses a Graph to compare the request object with the policy object.
Open the editor and paste the above model in the Model editor.
Paste the following in the Policy editor:
p, alice, sub-reader, sub1
p, bob, rg-owner, rg2
// subscription role to subscription action mapping
g, sub-reader, sub-read
g, sub-owner, sub-read
g, sub-owner, sub-write
// resourceGroup role to resourceGroup action mapping
g, rg-reader, rg-read
g, rg-owner, rg-read
g, rg-owner, rg-write
// subscription role to resourceGroup role mapping
g, sub-reader, rg-reader
g, sub-owner, rg-owner
// subscription resource to resourceGroup resource mapping
g2, sub1, rg1
g2, sub2, rg2
And paste the following in the Request editor:
The result will be:
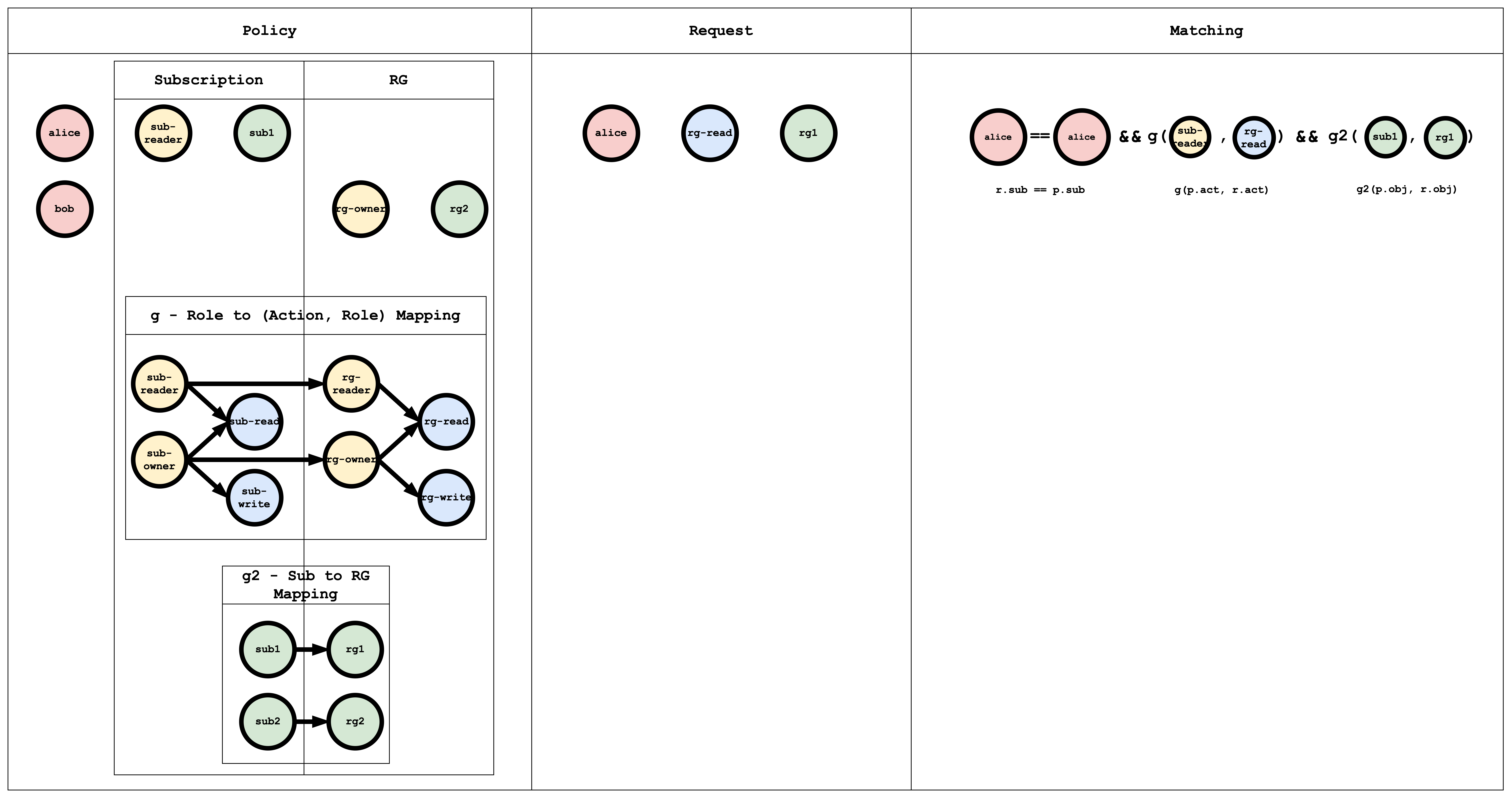
The g - Role to (Action, Role) Mapping table has a graph mapping the role to the action, role mapping. This graph can be coded as a list of edges, as shown in the policy, which is a common way of representing a graph:
// subscription role to subscription action mapping
g, sub-reader, sub-read
g, sub-owner, sub-read
g, sub-owner, sub-write
// resourceGroup role to resourceGroup action mapping
g, rg-reader, rg-read
g, rg-owner, rg-read
g, rg-owner, rg-write
// subscription role to resourceGroup role mapping
g, sub-reader, rg-reader
g, sub-owner, rg-owner
The g2 - Sub to RG Mapping table has a graph mapping subscription to resourceGroup:
// subscription resource to resourceGroup resource mapping
g2, sub1, rg1
g2, sub2, rg2
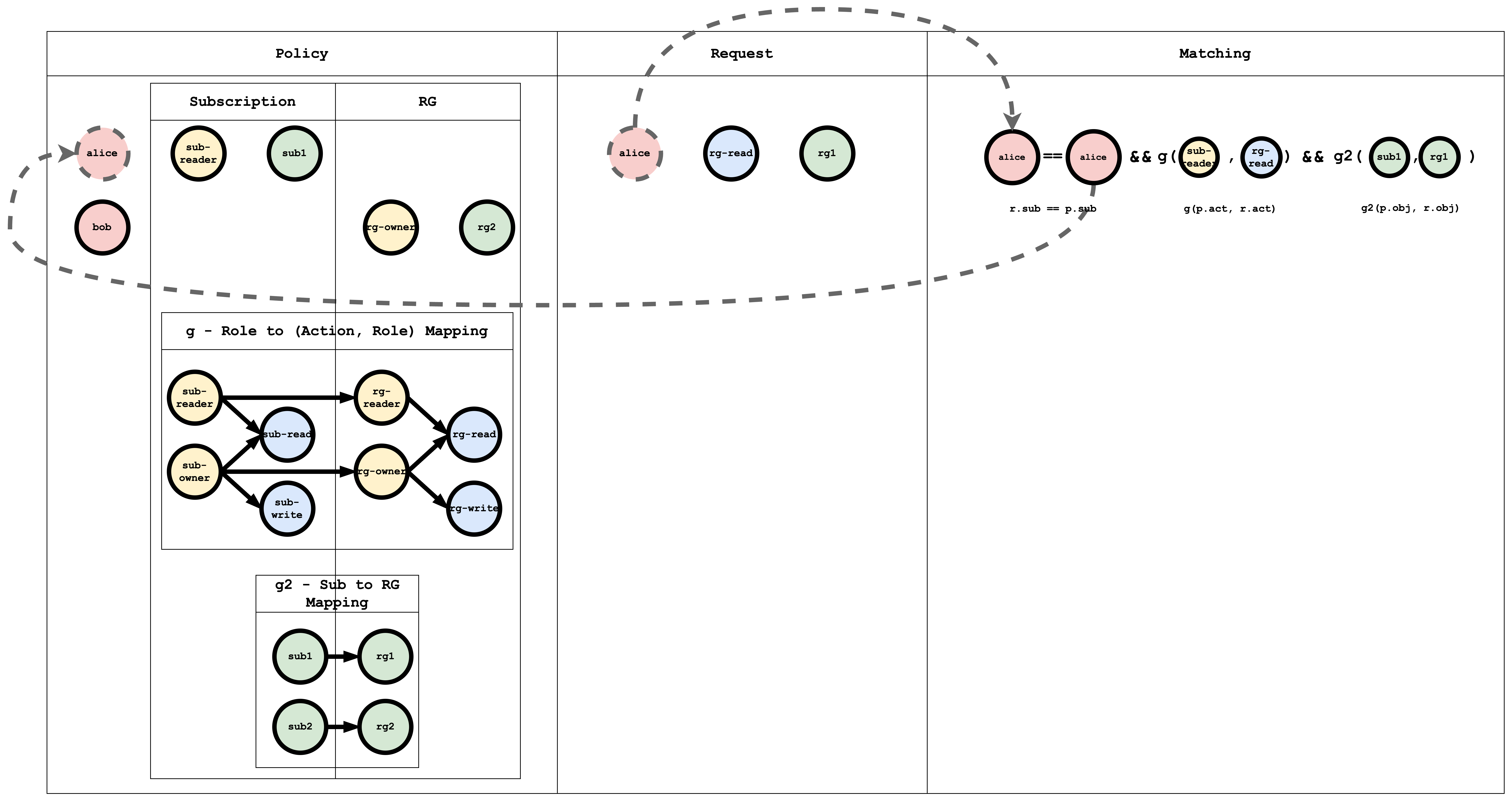
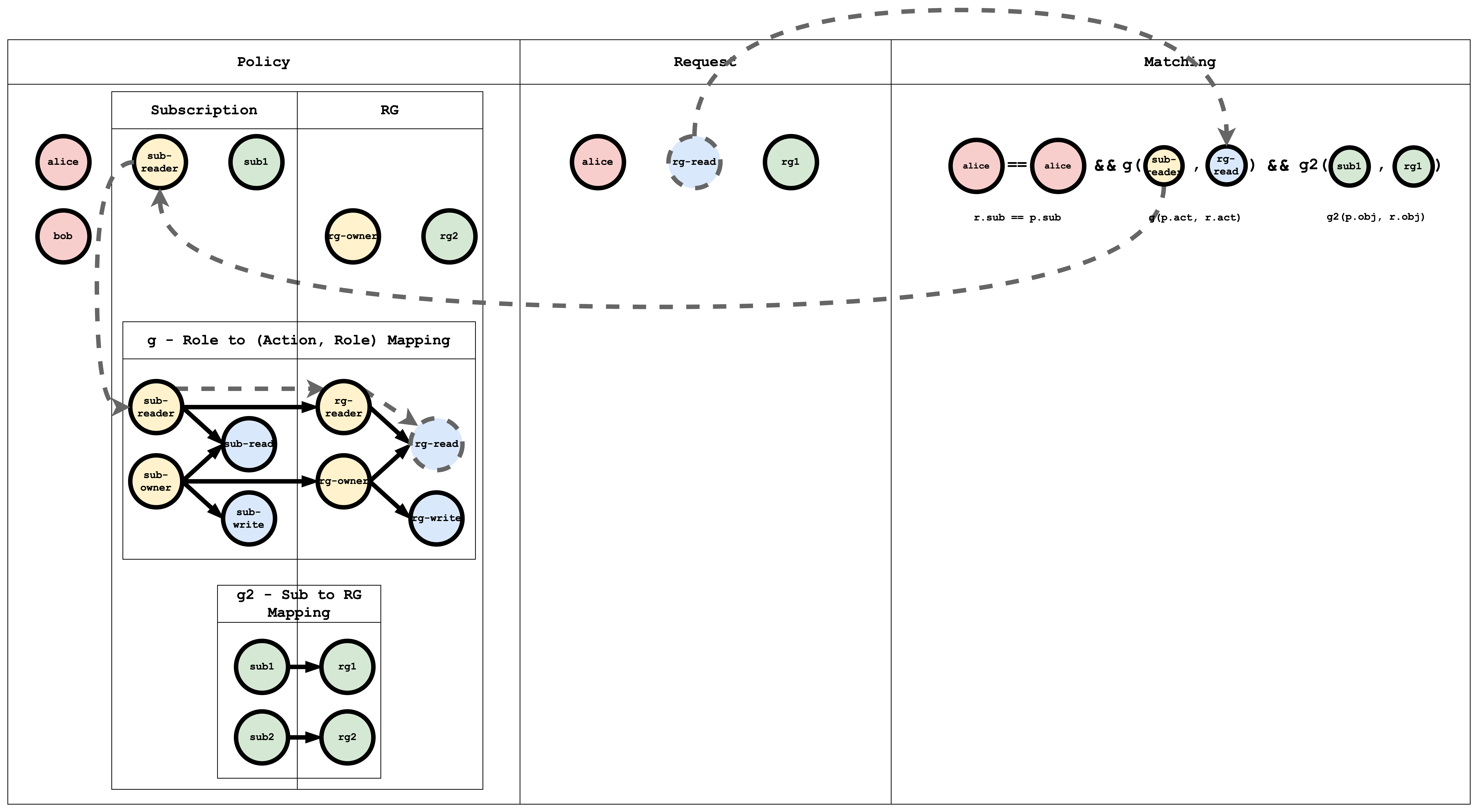
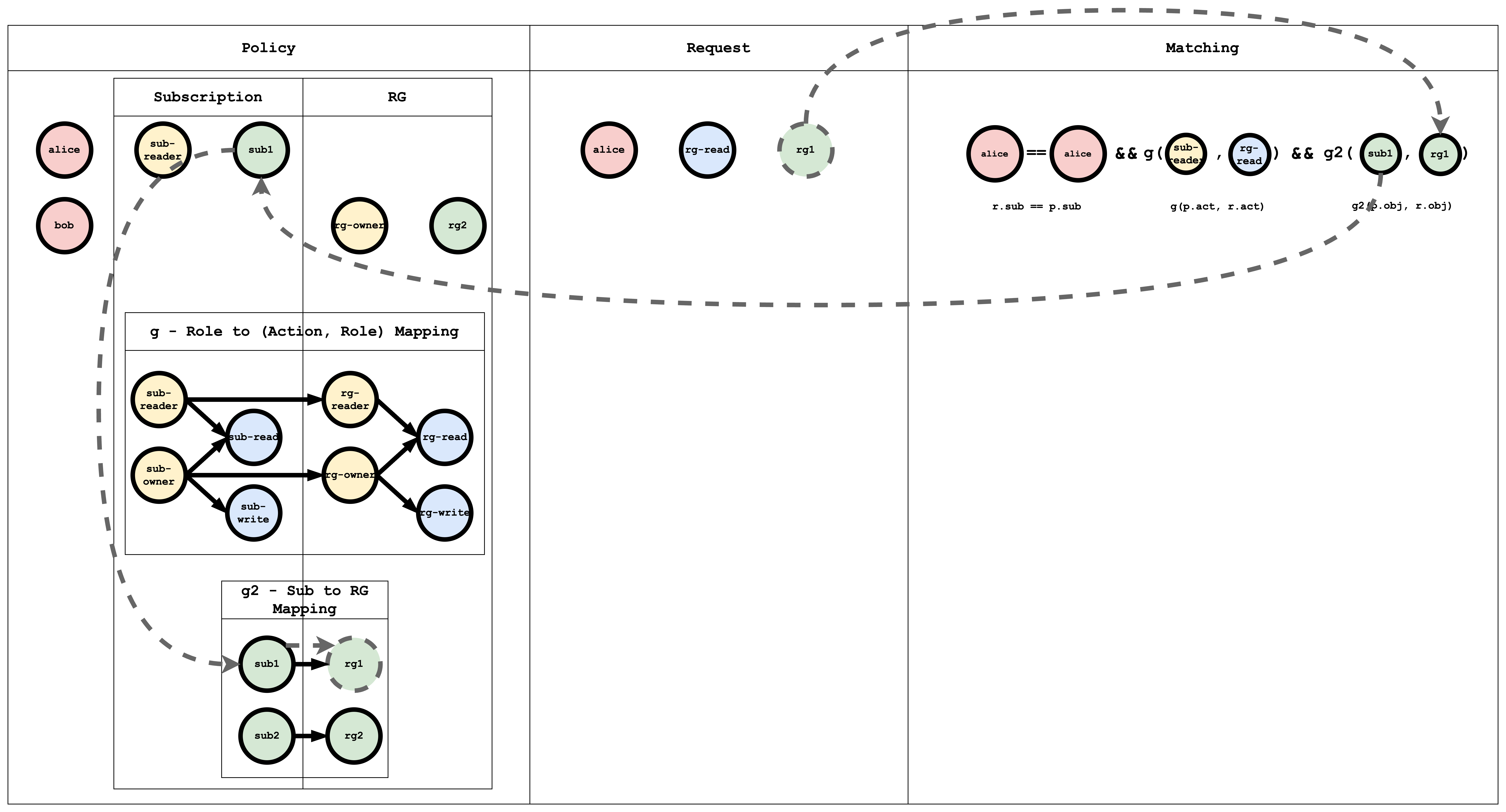
When a request is submitted to Casbin, this matching happens for all the policies. If at least one policy matches, then the result of the request is true. If no policy matches the request, then the result is false.
In this tutorial, we learned about how different authorization models work and how they can be modeled using Casbin. In the second part of this tutorial, we will implement this in a demo Spring Boot Application and secure the APIs using Casbin.